Development and Deployment using key-based authentication
This guide explains how to use key-based authentication both in the development cycle and with deployed splinter nodes.
Overview
For certain applications, splinter’s REST API authentication and authorization system requires an authorized public key in order to access various endpoints. These applications include daemon processes and other applications where access is not tied to a single user. They also include CLIs whose operation are tied to a user, but unable to use other authentication methods, such as OAuth.
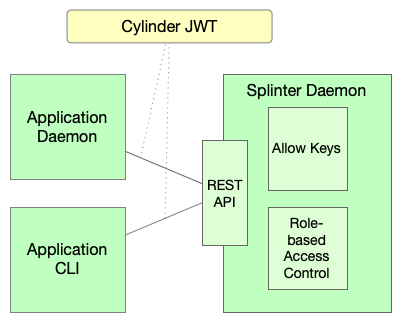
Non-user applications
In the case of non-user applications, such as a daemon process, the application should have its own public-private key pair. The application may be allowed to access any API with all permissions, or an administrator may wish to restrict the application to a constrained set of endpoints and permissions.
In the first case, the key pair may be authorized by placing its public key in
the allow_keys file. This grants all available permission to the key pair.
This is also very useful at development time for quickly configuring a local
node for testing purposes.
In the second case, the public key may be used as an identity in splinter’s role-based authorization control (RBAC) system. In that system, roles can be created with the desired permissions and assigned to the key pair.
User applications
In the case of non-user applications, such as a CLI tool, each user should have their own public-private key pair. The application for that user may be allowed to access any API with all permissions, or an administrator may wish to restrict the user to a constrained set of endpoints and permissions.
As in the non-user application, the first case is covered by putting the user’s
public key in the allow_keys file. This grants all available permission to the
user. This is also very useful at development time for quickly configuring a
local node for testing purposes.
In the second case, the user’s public key may be used as an identity in splinter’s RBAC system. The user can be assigned a role that is related to the application in question. With user keys in a production scenario, this method will be more desirable.
For example, a CLI tool called circuit-reader could have a corresponding role
of the same name. This role would be assigned the permissions needed to read
roles via the splinter REST API. Each user authorized to use the tool would have
the role assigned to their public key identity.
Using Key-based Authentication
Regardless of application type, any calls to the splinter REST API should
provide a Cylinder JWT, signed with the authorized key pair. This JWT token is
sent as the value of the Authorization HTTP header.
Authorization: Bearer Cylinder:<encoded Cylinder JWT>
See Also
Follow the guide for Configuring REST API Authorization for more information.